How Are Different Industries Utilizing AI and Robotics?
April 15, 2021
How Automation Technology Is Changing the Way Businesses Operate
April 22, 2021The data center industry has made more of an effort to lessen its power consumption. The industry has been incorporating different technological advancements including artificial intelligence and new cooling systems that have improved data center operations power consumption. Since 2010, computing capacity and workloads increased by 600% and internet traffic has grown 1000%, while data centers only increased their energy usage by 6%. Data centers are more efficient than most people realize, but the industry is looking to be even more efficient now and in the future.
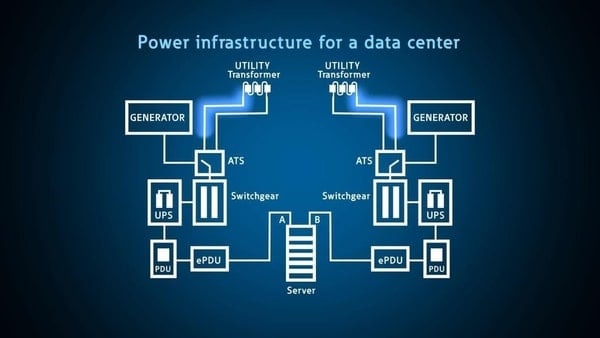
What Is Data Center Power Redundancy?
Many different industries rely on data centers for their everyday operations. Data centers need to be ready and available no matter what happens. Power outages can be caused by many different things including extreme weather conditions, grid failures, natural disasters, rolling blackouts, electrical failures, and other things that can cause a data center’s power to be interrupted. All businesses, in every industry, expect data centers to have uninterrupted power 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. This is why power redundancy one of the crucial aspects of data center operations.
Power redundancy is a system designed for the reason of in the event of a power outage the data center will not be impacted. A data center that has a redundant power supply operates by using two or more physical power supplies. All of these power supplies have the capability of running on their own so no matter what happens a data center will be able to keep going.
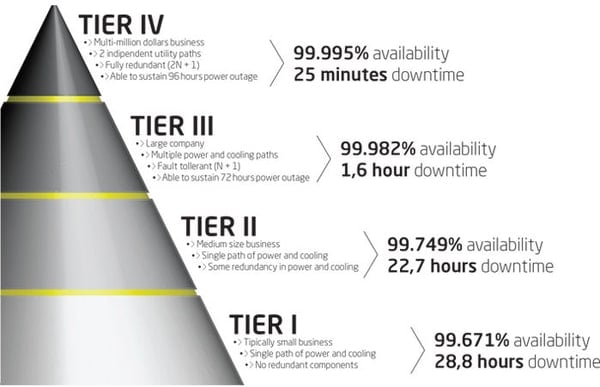
What Is the Data Center Reliability Tier Standard System?
There are data center standards that evaluate the quality and reliability of each data center’s server hosting ability. The Uptime Institute has created a four-tier ranking system to rate the specific expectations and benefits of each data center. A Tier one data center is the lowest tier and is normally utilized by smaller businesses. Tier 1 data centers are required to have 99.671% uptime. Redundancy isn’t required and businesses can expect about 28.7 hours of downtime each year.
A Tier 2 data center is required to have 99.749% of uptime. It is required to have partial redundancy for both power and cooling, but companies can expect to experience around 22 hours of downtime per year.
Many large companies tend to utilize the power and resources of Tier 3 data centers. In this tier, businesses can expect at least 99.982% of uptime. These data centers are also required to have no more than 1.6 hours of downtime per year. Tier 3 data centers are also N+1 fault tolerant providing at least 72-hour power outage protection.
The last is the Tier 4 data centers, which are typically used by enterprise corporations. These data centers are required to have 99.995% of uptime per year, 2N+1 fully redundant infrastructure, and 96-hour power outage protection. Companies that use a Tier 4 data center should only expect about 26.3 minutes of downtime each year.

What Is the Problem with Diesel-Powered Backup Generators?
Because data centers require uninterrupted power (or as close to it as possible), backup generators are set up to take over when there is an interruption of the main power source. Data center backup generators have long been powered by diesel engines. As the world continues to deal with global warming, most industries are looking to go green. Because of its environmental impacts, data centers need to monitor these diesel-powered backup generators for emissions including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter.
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that is produced from the inadequate burning of fossil fuels. It’s odorless and colorless, which makes it even more dangerous. Nitrogen oxide is a non-toxic gas that is also colorless. It happens as a consequence of the bacterial process, decay, burning of fossil fuels, and biological growth. Hydrocarbons are chemical compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen. They can come in various forms such as methane or polystyrene. All of these need to be monitored because of their effects on humans and/or the environment. The burning of fossil fuels emits multiple air pollutants that can are harmful to the environment and people. Limiting these pollutants is a main focus for the data industry.

Can Data Centers Run on Battery Power?
Data centers are becoming more energy efficient using renewable energy such as water, wind, and solar energy. But although there have been advancements in these renewable energies, data centers are primarily still using diesel generators. There are several reasons why backup generators use diesel. Compared to other forms of fuel (liquid propane or natural gas), diesel-powered generators have lower costs, they also need less regular maintenance, and are one of the more efficient sources of fuel.
Some major technology companies have already switched over to Lithium-Ion batteries as their main source of energy. Traditionally, lithium production costs are expensive which has made lithium batteries an expensive alternative energy option. But due to the coronavirus pandemic, the prices of lithium have dropped. Even before the current pandemic, many industry experts believed the prices of lithium would drop.
Lead batteries have been used for backup power sources because of their ability to provide high power over long periods. This is necessary for a data center’s Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system. But advancements in Lithium batteries can quickly discharge large amounts of energy and charge quicker. This eliminates the need for a longer-lasting power supply. Modern Lithium batteries are not performing at an efficiency of 99% only losing 1% of stored energy for 24 hours. This makes it perfect for the main power supply as well as a backup energy supply.
Conclusion
Battery technology has come a long way in the past decade. Modern Lithium-ion batteries have become the best and cleanest solution for data center operations. As the data center industry continues to push its environmentally-conscious initiative, data centers may transition to this cleaner energy. Although diesel power is still more affordable than its battery counterpart, Lithium prices have gone down and may continue down this trend. If this is the case, data centers may be able to solely run on battery power in the near future.
