
The Future of Gaming Is Not a Box. It’s a Data Center
November 12, 2019
How Face Verification Could Reduce Data Breaches?
November 13, 2019While laying out the foundation for a website, most site developers tend to prioritize getting applications up and running, instead of focusing on the security aspect of the website’s infrastructure.
Taking into consideration the ever-evolving threat landscape of today, some cybersecurity specialists and researchers might even go as far as to say that server security should be treated as a priority, rather than a last-minute “IT expense.”
With data breaches haunting each enterprise, small business, and organization, the threat facing website hosting providers and server administrators have increased exponentially. Long gone are the days when website hosts could get away with hosting insecure servers, and not suffer the consequences of their carelessness.
To aid our readers in the tedious process of securing website servers, we’ve compiled an article that delves into some of the more fundamental server security tips to get them started on the lengthy (but also achievable) path to online security.
Security Tip #1- Firewalls
As far as servers are concerned, services are usually divided into three groups, namely public, private, and internal services. As their names suggest, public services refer to those services that can be accessed by anyone with an internet connection, whereas private services are only accessible to a select group of authorized individuals. Internal services, on the other hand, should only be accessed from within the server, without being exposed to any third-party.
When it comes to increasing server security, a firewall can play a critical part in ensuring that access to services goes according to the categorization they’ve been placed in. If a properly configured firewall is implemented within a server, not only does it act as an additional layer of security, it allows for public services to be accessed by anyone while blocking any access to internal services.
By blocking and restricting the outside world’s access to internal services, the chances of a data breach or hack lower significantly, since the surface area of exposed software diminishes, and effectively lowers the components of a server which are vulnerable to exploitation.
Another rather unique advantage of integrating a firewall into a server is that they are quite simple to implement and take no more than a couple of minutes to set up. Some popular choices for firewalls include the Config Server Firewall (CSF) and the UFW firewall.
Security Tip #2- Service Auditing

Credit: ISO
A significant part of server security or even cybersecurity in general, which is often overlooked, is analyzing existing security measures and working on improving them.
Although there’s been a recent wave of VPN providers getting their servers audited by independent third-party security auditors, the trend is yet to reach the more mainstream canon of cybersecurity practices. For the most part, most site developers and server administrators are unaware that such a practice even exists.
Simply put, service auditing, similar to security auditing, is a practice that allows the people in charge to know the specifics of the services running on their systems. Such information usually includes details on the ports being used for communication on the network, along with the protocols being accepted. The information that comes out of a service audit proves to be extremely fruitful in configuring a firewall as well.
Service auditing does many things for server security. However, the primary advantage it offers is the chance to limit the number of services being run on the network. As we’ve already mentioned above, the greater the number of running services, the higher are the chances of vulnerabilities to exploit the software.
After the audit is complete, and you’ve got the valuable knowledge that you need, you can analyze which services you need and which services you need to get rid of. With that said, try to make these service audits routine, rather than performing them once in a blue moon.
As far as the implementation of the service auditing practice is concerned, an essential service audit can be performed by almost anyone- by merely using the netstat command, to gain insights into active services and ports.
Security Tip #3- SSH Keys

Credit: SSH.com
As a general rule of thumb, consider encryption to be the stepping stone for the other security measures that you can implement into a server. A security tip that allows for the encryption of authentication measures into a server is known as the SSH keys.
SSH keys are a couple of cryptographic keys that consist of two main components; a private and a public key. The pair of the SSH keys are then used to authenticate the identities of individuals wanting to access a server and serve as an alternative to password-based authentication methods.
The working behind the creation of SSH keys dictates that the private key is kept secure by the user, while the public key is to be shared by anyone and is kept in a unique directory. When a client requests access to the server, the server will ask for proof of the private, which will then be provided by the client.
If the client proves his identity and possession of the SSH private key, the server lets him/her access the server without the hassle that comes along with a password-based authentication approach, along with the added benefit of the entire authentication process being encrypted by the popular RSA-2048 bit encryption method, which is equivalent to a 617 digit password.
From a security perspective, the integration of SSH key authentication eradicates the need for password-based logins. Through a password-based authentication system, malicious identities can gain access through a loophole, or automating their attempts to break into the server by eventually cracking the password.
Moreover, similarly to all the measures we’ve mentioned up to this point, setting up an SSH keys authentication is generally quite easy and can be accomplished within minutes.
Security Tip #4- Implement a Robust and Sophisticated Password Strategy
Even though the introduction of SSH key authentication opens up multiple avenues as far as alternatives to password-based authentication methods are concerned, it’s quite understandable why some people might want to opt for the more traditional authentication method.
In the instance that you acquire a new server, it is highly essential that you implement a complex password strategy; otherwise, you’ll have to face the bleak consequences of having malicious third-party gain access to your server.
Although we’re personally in favor of organizations ditching passwords logins altogether for the more secure SSH key-based authentication- there are still some ways through which organizations can implement a strategy that maximizes the security of password-based logins.
The first step in achieving a vigorous password policy is by using a random combination of letters (lowercase and uppercase), symbols, and numbers to formulate passwords. The second step in the implementation of a robust password policy is to frequently update or change the passwords being used to access the server.
Also, it’s worth mentioning (considering that people still use passwords like ‘qwerty’ and ‘iloveyou.’) that as a general rule of thumb, stay away from passwords that contain any personal information, or the information of a loved one.
Despite the initial difficulty that users face in remembering complex passwords, the most that the implementation of a complex password strategy requires is dedication from the employees of the organization- which makes them pretty easy to integrate into the security infrastructure of an organization.
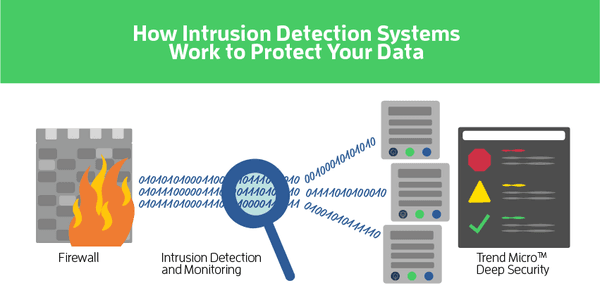
Security Tip #5- Setting up Intrusion-Detection Systems
Credit: Atlantic.Net
We’ve already gone through the perks offered by service auditing, including the ease it provides in configuring the firewall settings. Similarly, another analytic security measure is file auditing, which compares the current network components, with the previous elements of a system, when it is in a “known-good” state.
File auditing plays a vital part in server security and lets you know whether or not the changes made to the system have been authorized. An intrusion detection system, on the other hand, works similarly and surveys incoming and outgoing traffic for any unauthorized activity. Some IDS (intrusion detection systems) also integrate file auditing into the software to confirm whether an authorized change has been made to the system.
Although the processes involved in setting up intrusion-detection systems can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, the benefits offered to outweigh the tedious configuration. Not only do they detect when a malicious identity has gained entry to a server, but they also allow users to be confident of the integrity of their server, right down to each file.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, users can also resort to the use of more modern technologies such as AI and Machine Learning to propagate the principles of cybersecurity to servers as well. Both AI and ML are quickly becoming staples in the security industry.
Security Tip #6- Create Back-Ups
When compared to the other server security tips we’ve included, even the notion of asking our readers to create back-ups of their data seems redundant at best, (at worst; a lazy attempt by us to increase the word count), but it’s a mistake we’ve seen thousands of time.
Unless you want history to repeat itself, it’s essential that you create routine back-ups of the data stored on the server, including an immaculate plan of extraction in the instance that your data gets compromised in the event of a data breach.
Furthermore, ensure that you’ve got access to a secure storage facility for off-site back-ups.
If you follow all the steps mentioned above, you can be assured that you can avoid 99% of all the server related threats and can stop hackers from invading.
It’s an essential matter of being careful and disciplined rather than being utterly carefree while you’re using your system. As the saying goes, it’s better to be cautious than to suffer the consequences of having your system exploited by malicious agents.
Main Image Credit: Forbes
