
Why Biometric Authentication Is Stronger Than Passwords
August 7, 2018
What’s New in the World of Data Storage
August 16, 2018Edge computing is one of the new buzzwords in technical jargon. It’s what “the cloud” was when the cloud was first conceived. In actuality, there are some definite similarities between cloud and edge computing.
As we continue to use our mobile devices—we will continue to retrieve data from either the cloud or from edge computing. But because the cloud is centralized in a separate location, we will often find ourselves experiencing latency issues, especially when dealing with more intensive data. Many people will experience latency issues when dealing with audio, video, etc. As the physical distance between the user and the cloud increases the more transmission latency issues the user will have.
What Is Edge Computing?
The way edge computing works is by adding an additional platform that positions itself between the cloud and the user. Some of the applications and data are housed here instead of everything coming directly from the cloud. The most important aspect of this is that the location of the edge computing platform is physically closer to the user. This helps everything process faster because not everything is coming directly from the cloud or the device. This helps speed up the applications on one’s device.

Photo Source: Data Center Frontier
What’s the Difference between an Edge Network Vs. Cloud Network?
Some people believe that edge computing will take the place of and make the cloud obsolete. The truth is that these networks can work symbiotically. The use of both will allow less strain on the other and both networks can benefit from each other.
What are the Differences between FOG Computing Vs. Edge Computing?
Edge helps bring processing power closer and directly to the data source. It doesn’t need to be sent to a separate cloud or any other centralized system to be processed. By bringing the power directly to the user—Edge improves the speed and overall performance of the data transport. It also improves the performance of the device using Edge computing as well.
FOG computing is an older term that pre-dates edge computing. Many consider FOG computing as the standard of how Edge should work. While Edge computing drives the processing power of an edge gateway directly into devices, FOG drives intelligence down to the local area network and processes it by a fog node or IoT gateway.
The main difference between the two is where the intelligence and power are pushed. But because FOG computing and Edge computing both drive the processing capabilities closer to the user—many people use FOG and Edge synonymously.

Photo Source: Virtualization Review
What Are Some Edge Computing Examples?
Drones, robots, and driverless are becoming more of a norm (well, at least the first two). And these devices can accumulate a tremendous amount of data and use a copious amount of processing power. They also require low-latency connectivity. These devices are great examples of what edge computing can be the most useful for.
Vapor IO and Hangar Technology have collaborated to create a prototype robot-powered world with an edge infrastructure. They are projecting there will be drone stations across the nation, but the first one is slated to be located in Chicago, IL.
Hangar Technology, Vapor IO, and Project Volutus are expecting 40,000 wireless sites across the US. They are also planning to have 27 Kinetic Edge nodes by the end of 2018, and an additional 100 nodes by 2019.
The same way that electricity required an electrical grid to transform the economy—autonomous robotics requires new automation grid to change the infrastructure again. This new project is a great example of how Edge computing works in the real world and a glimpse of what the future may look like.
What Is Edge Networking? How Will It Reshape Data Centers?
The research firm, IDC, reports that 45 percent of data created by IoT will be stored, processed, analyzed by edge computing. And by 2020, more than 5 billion devices will be connected to the edge network. Because of this, many businesses will change the way they operate.
One industry that will see a major change is the data center industry. Data centers, as we know it will change because of Edge networking. IDC researchers predict that micro-data centers will be built into existing towers. These micro-data centers will handle data similar to the way current data centers manage information. And business customers can rent out space to enable Edge computing. We will these smaller data centers closer to every business in the future, and latency issues could be a thing of the past.
As mentioned earlier, I believe these network advancements won’t cancel each other out. The cloud, Edge networks, and data centers all have a place in the realm of data management. In fact, as they work together, the way we retrieve our data will be faster and stronger than ever before. And this will be extremely important when incorporating IoT systems.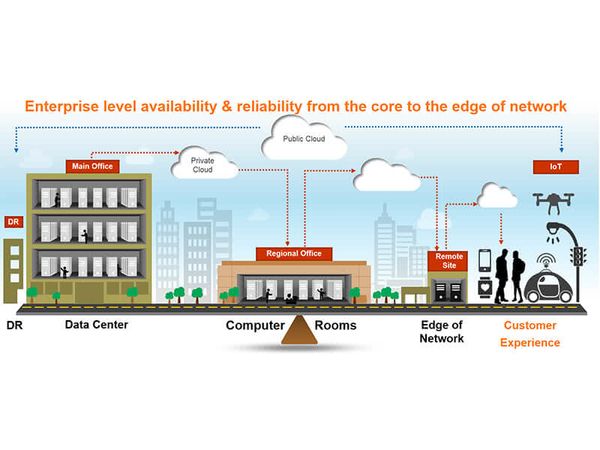
Photo Source: Virtiv
What’s the Latest News in Edge Computing?
As we see an increase usage rate in IoT devices, the need for edge computing will rise steeply as well. The concept of a robot powered world and an automation grid infrastructure is the latest and most exciting news in the world of Edge computing. This grid will help many different businesses and companies in real-time. While this concept is in its early stages—the future looks bright.
Conclusion
As our technology gets more and more advanced—the network that these devices are on needs to become more advanced as well. It seems as though Edge networking will certainly be a part of data management in the future. Edge brings the network closer to the users and eliminates latency issues. It will also help streamline the flow of traffic from smart devices within IoT systems. Although people once thought Edge would displace the Cloud—it is more likely they will work together to make our lives easier.
