Disaster Recovery Trends for SMBs
January 16, 2013
Online Data Storage: Backup Made Easy
January 18, 2013Utilizing a high-availability or Load Balancing server setup will ensure your website stays up-to-speed no matter what.
Guaranteeing that a website is always up and running for people to browse, buy from and enjoy is ultimately what every webmaster would like to claim.
There have been many instances in the past where there is so much demand on a website that the server crashes and becomes inaccessible and completely unusable.
This usually doesn’t happen to any plain old website. There needs to be a lot of traffic directed to it in a short period of time. We commonly see this in websites that have some kind of special offer running, or a great ‘deal’ that expires within a very short amount of time. Once a lot of people start trying to access a website at the one time, things become too much for the server to handle and everything comes to a grinding halt.
Hosting your web applications and/or websites on a single server leaves you open to a single point of failure, placing you at risk of having your server crash due to extremely high amounts of traffic. There are two ways to keep your server running without any downtime: Load Balancing or High Availability.
Load Balancing
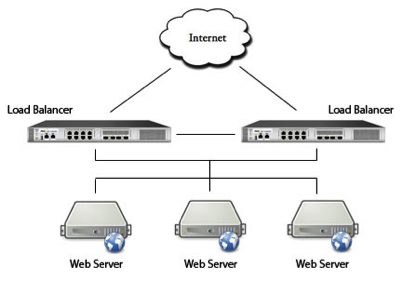
Load balancing is simply a set of servers in which the traffic is evenly spread between them to help reduce the load on a single server. An application delivery device is needed to do this, such as A10’s AX Series Application Delivery Controller. For example, if 5000 people are trying to access a website and you having load balancing set up between two servers, then 2500 people will be directed to each server, helping to spread the load to gain optimal efficiency of a server, and to help stop a server from crashing. The more load balanced servers that are set up, the more the load can be spread out between them.
High Availability
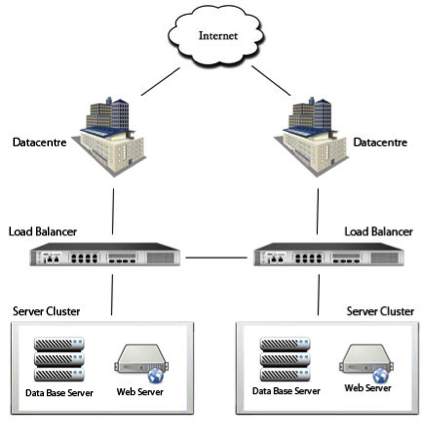
High availability is a form of Load Balancing where you have multiple servers running simultaneously in a primary/secondary arrangement. If traffic to the first server gets too much and the primary server goes down, the secondary servers becomes active and would then deliver your content without anyone losing connection to your site or application.
The degree of‘high availability and load balancing’ is determined by how much money one is willing to invest in ensuring that their website is not going to go down as a result of spikes in traffic. The best way to ensure your site doesn’t go down is to do the following:
- -Run Load Balancing and/or HA on multiple servers
- -Run this over multiple data centres
- -Run them over multiple networks
This is generally an expensive option and not many companies in the world can do it (due to the multiple networks), but the ones that can do ensure that even if an entire data center, or even an entire network were to go offline for some reason, then delivery of your content would continue to run.
To give you an idea, some load balancing devices are able to handle up to 300, 000 concurrent sessions! Obviously these systems are only needed by websites and applications that have enormous quantities of traffic. However, if you do have a website that generates so much traffic it is a good idea to invest in Load Balancing and/or High Availability to seamlessly deliver content to your users without any hiccups.
This is an example diagram of geographically redundant high availability.
This is an example diagram of basic High Availability with multiple web servers
About the author: Alex Burgess works in marketing for Servers Australia, one of the leading web hosting companies in Australia. He manages and is one of the main writers for their blog.