
The Battle of Supercomputing
March 20, 2023
Will There Be Data Centers on the Moon in 2023?
March 27, 2023Most people rely on vision for everyday tasks including walking around, reading street signs, preparing and consuming food, doing tasks for work, reading articles like this one, and hundreds of other tasks. Vision is the highest bandwidth sense and provides information about what is around us and how to act appropriately. Because vision is an essential part of our everyday lives, computer scientists have tried to give computers this same sense for many years.
Computer vision aims to give computers the capability to of high-level understanding from digital images and videos. It looks to give computers a similar level of understanding of images as humans do. Everyone with a smartphone or tablet knows that these modern computer devices are already great at capturing images with astonishing detail. But the ability to capture these images isn’t the same as applied human vision. This is where computer vision becomes even more intriguing and useful.
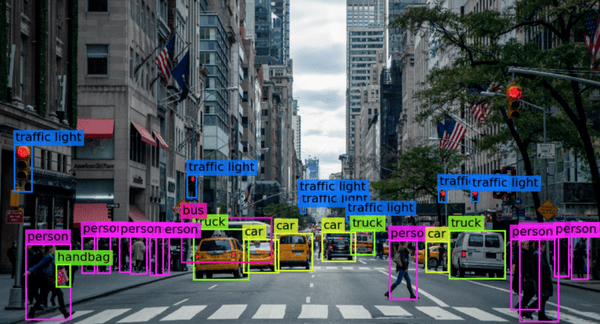
How Can a Computer Have “Vision?”
Computer images are typically stored as large pixel grids. Every pixel is defined by a specific color and stored as a combination of the three primary colors red, green, and blue. Combining various concentrations of the primary colors gives computers the RGB value, representing all the colors in the spectrum.
An essential aspect of how computers can distinguish what is in a photo is what’s called convolutional neural networks. A convolutional neural network, or CNN is a type of artificial neural network used in image recognition. The convolutional neural network uses a method specifically designed to process pixel data. The CNN uses multiple filters to find specific features in the image for object categorization. Various kernels are responsible for extracting and delineating these features. It highlights differences in pixel values. The analysis of these images is processed with a grid-like topology.

What Are the Various Aspects That Makeup Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is a fascinating aspect of artificial intelligence because it aims to allow computers to see similarly to humans. It is a part of computer science that concentrates on imitating the parts and complexities of the human visual system to enable computers to identify and process objects in videos and images similarly to humans.
Innovations in artificial intelligence, deep learning, and artificial neural networks are making this possible. These computer science systems could even surpass human vision in the way it detects and labels particular objects. Here’s a quick recap of AI, deep learning, and neural networks.
Artificial intelligence is the ability of a computer or a computer-controlled robot to do the tasks that humans typically do. Human intelligence and judgment are emulated by artificial intelligence.
Machine learning is the process of data analysis that automates analytical model building. Machine learning is a specific branch of AI founded on the idea that systems can learn from specific data by identifying patterns and making decisions with little to no human intervention. Deep Learning falls under machine learning which teaches computers to learn by example. Deep learning is one of the key technologies to autonomous vehicles by allows them to recognize a stop sign and distinguish a pedestrian from an inanimate object.
The final part of Computer Vision, which we mentioned earlier, is Neural Networks. Neural Networks are a series of algorithms that attempts to identify fundamental connections in a set of data through the process of mimicking the way human brains operate. It emulates the brain’s system of neurons artificially.
What Is Computer Vision?
So, what is computer vision? Artificial intelligence, deep learning, and neural network all work together to give computers the ability to “see.” All of these aspects work together in a couple of different ways, including categorizing objects in an image or recognizing digits. One example of computer vision that many people use daily is facial detection. We use it for security purposes in our digital devices, including our smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Computer Vision uses AI, deep learning, and neural networks to see and make decisions. The process includes various steps. The first step is detecting and finding objects within a particular image. The next step is finding the type of object and then extricating all pertinent info from the object. Next, the computer needs to figure out the location of the object within the computer vision system. Lastly, the computer needs to find specific patterns within the system.

What Can Computer Vision Currently Do?
There are several examples of Computer Vision being applied. IBM Watson, the company’s data analytics processor, used Computer Vision to sift through hundreds of hours of the 2018 Masters golf tournament to identify and curate key moments for a highlight reel. Google Translate also uses the technology to detect a particular language and translates it into the preferred language of the user’s choice.
As mentioned earlier, autonomous vehicles use Computer Vision technology in real-time to identify other cars, traffic lights, lane markers, people, and other modes of transportation that the car may meet on the road. It is also being used to bring intelligent AI to edge computing.
Image classification, objection detection, object tracking, and content-based image retrieval are the main aspects of what Computer Vision can do, but this is just the beginning. If computers can see, learn, and understand their surroundings like humans do, the possibilities are endless.

Conclusion
The world’s view of where technology can potentially go, especially in artificial intelligence, will rely heavily on Computer Vision. If we are looking for computer devices to make decisions, these computers will first need to “see” and discern what is around them. Autonomous vehicles will soon be more visible on the road, and when this does happen, we know one of the main reasons will be this Computer Vision. While this technology is still in its early stages—the potential of this Computer Vision is interminable.
