What Is a Data Architect?
September 1, 2022
What Is Solar 3.0?
September 8, 2022Table of Contents
- What Is Pervasive Computing?
- What Is Ubiquitous Computing?
- What Are the Advantages of Ubiquitous Computing?
- What Are the Challenges of Ubiquitous Computing?
- How Will Ubiquitous Computing Impact Data?
Computers have become an integral part of our everyday lives, and computing technology continues to advance and evolve in a variety of ways. It is estimated that more than 6.6 billion people use a smartphone, which equates to about 79 percent of the world. Through our smartphones and other smart technologies, we deploy technology like virtual reality, which puts its users inside of a computer-generated three-dimensional environment. Ubiquitous computing turns this around and brings the computer out into our world.
What Is Pervasive Computing?
The idea of having a computer being with you at all times, and even more so, everywhere you go is the basic idea of ubiquitous computing. We are already experiencing a basic level of this idea in the form of the Internet of Things or IoT.
IoT refers to the network of physical objects that have been implanted with the technologies that allow for connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems through the internet. The difference between IoT and ubiquitous computing is how users and devices are connected.
Pervasive computing enhances how we use computers by making network-connected computer devices available throughout our physical environment, and the same time making them invisible or at least unobtrusive. This can be deployed through our smartphones and other handheld devices, and even hidden in everyday objects such as furniture and clothing.
Pervasive computing can be beneficial for health care, environmental monitoring, smart transportation systems, and more. Pervasive computing ubiquitous computing can be deployed in just about every aspect of our lives.

What Is Ubiquitous Computing?
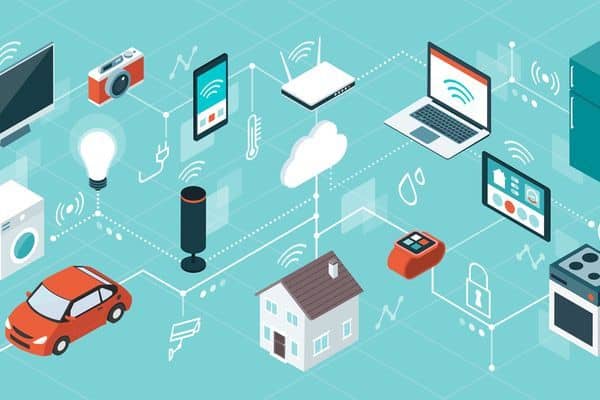
The terms ubiquitous computing and pervasive computing are often used interchangeably. The general idea of ubiquitous computing is embedding everyday objects with computational capabilities, so they can communicate with users and other ubiquitous computing objects. This minimizes the need for users to interact with computers as computers.
Traditional desktop computing devices are stuck on desktops, while pervasive computing devices can be anywhere at any given time. The ability to access data for business or personal has made remote working even more feasible. Our current pervasive computing devices allow us to move our work from home to the car, to the office without any slowdowns.
Current pervasive computing devices include laptops, smartphones, tablets, notebooks, and even wearable devices. Ubiquitous computing is regularly thought of as the successor of mobile computing. Wireless communication and networking technologies have made this type of computing and remote work possible. It typically uses additional technologies such as embedded systems, RFID tags, voice recognition, and artificial intelligence.

What Are the Advantages of Ubiquitous Computing?
The basic end goal of technologies such as the Internet of Things and ubiquitous computing is to make their users’ lives simpler. Through these ubiquitous computing devices and tools—users can manage data and information more easily. Users can use portable devices to connect where they need to connect from anywhere in the world.
In the future, ubiquitous computing could potentially be invisible technologies that don’t look like traditional computing devices. Many individuals have already transitioned away from desktop computers to wireless devices that can be brought anywhere. Soon, we could see another transition into more invisible computational devices that allow users to connect in even more places.
The future advantages of ubiquitous computing will enhance user experience, allow users to manage information more efficiently, and allow users to work from anywhere and at any time. Future ubiquitous computing could look and feel more like the Internet of things allowing users to connect from any location even without their own devices.

What Are the Challenges of Ubiquitous Computing?
The first challenge to ubiquitous computing is adoption. When a new technology is introduced, the usability and learning curve could potentially be steep. Learning new technology (even one that is a tangible device like a desktop) can already be difficult for many individuals, but a technology that is embedded in other objects and is invisible can potentially be even more difficult to use for some individuals.
Once users have gotten past the point of adoption, the next biggest challenge when it comes to connected technologies such as ubiquitous computing is security and privacy. There will be privacy and security issues with most new connected devices. This is an issue that will need to be taken care of as the technology becomes more embraced.
Lastly, new technologies can be expensive for users. As ubiquitous computing continues to gain traction, the price of ubiquitous computing may be too expensive for some users. Once the technology has been around for some time, the prices will go down and will become more affordable to more people.

How Will Ubiquitous Computing Impact Data?
Ubiquitous computing will create a tremendous amount of data. If each smartphone user creates about 60 gigabytes of data every year, and there are over six billion smartphones—this creates more than 335 exabytes of data every year through smartphones. This doesn’t even count all of the laptops, tablets, and other smart connected devices.
Internet of Things devices is expected to create about 73.1 zettabytes of data by 2025. To put this into perspective, a zettabyte is equivalent to one trillion gigabytes. Because ubiquitous computing will incorporate technologies similar to smart devices and IoT devices—the data that will be created will continue to grow exponentially.
As the world deploys more connected devices through the Internet of Things and ubiquitous computing—data centers will be even more essential than ever. Edge computing will also play a large role in how these technologies are connected. Not only are these technologies connected, but they will also deploy artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to enable the idea of invisible ubiquitous computing.
The rise of connected technologies and ubiquitous computing shows how important the data center industry is and will be in the future. As we go towards the concept of invisible technology that seems to just work for its users without the tactile input like traditional desktops—data centers will be at the center of this ecosystem. Harnessing the power of a data center and its connectivity will be important for many businesses today and in the future. If you are looking to get started in a data center, Colocation America has all of the data center services and connectivity your business may need. We offer colocation services, dedicated servers, cloud connectivity, managed server hosting, and more. Connect with Colocation America today.