
10 Tools to Prevent DDoS Attacks
October 24, 2018
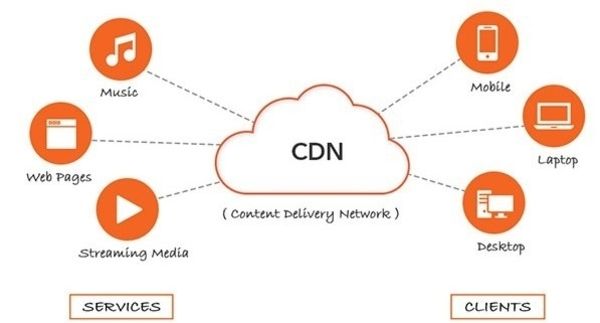
What Is a Content Delivery Network?
October 30, 2018If you work for a large company that has a popular website with high traffic, the chances are that your company is using a CDN. What is a CDN then? To put it simply, content delivery network (CDN) is a network of servers that are located in data centers around the globe.
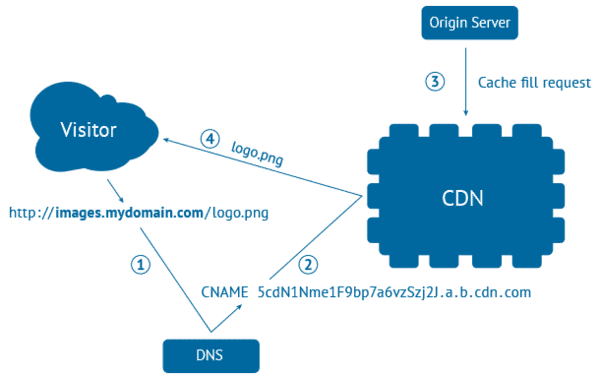
The CDN caches content from your website, for example, HTML pages, images, videos, and JavaScript files, which are stored in each server. When users load the webpage, they receive these files from a server that is geographically the closest to them.
Using a CDN can have a strong impact on your website and services. It can increase your website’s speed, improve performance, and make sure that all users have the same high-quality experience, no matter their location. https://www.youtube.com/embed/GCkbJh4vUzsIn case you’re interested in learning more about how CDNs work, you can check our earlier post about CDNs and why you need them.
If you’re in the stage where your website has started to grow and receive more traffic, it’s time to think about getting a CDN. As always, there are both advantages and disadvantages of using such a service. Let’s take a closer look at them.
Advantages of Using a CDN
Faster delivery of content
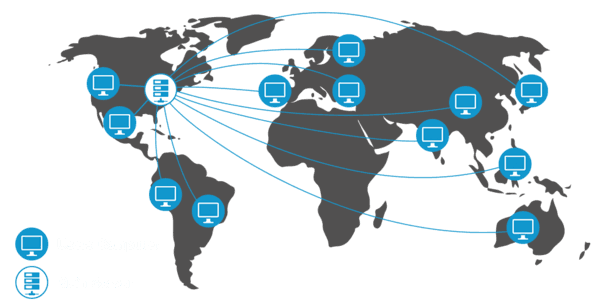
Because CDNs are placed closest to the user, it’s possible to reduce latency when the distance that your content needs to travel is shorter. A CDN can make your website load much faster. For example, if your website is based in the UK and you get traffic from the U.S., it’s possible that your CDN provider has a server in the U.S. and will use that server for your website.
More simultaneous users
A CDN can ensure that a network has a high data threshold. A large number of users can thus access the network at the same time without delays. By enabling a high traffic flow, CDN allows people from all over the world to access your website simultaneously.
Constant availability
Servers in the CDN are always running, and your website is accessible even if your server is down. Without a CDN, your server can sometimes be down which means that you have to wait until your host fixes the problem. This cannot happen if you’re using a CDN. In case of a crashed server, the CDN will use your cached pages.
Reliable delivery of content
The delivery of content is more consistent if you’re using a CDN. In particular, this concerns high-resolution content such as videos and images. CDNs provide high-quality content delivery and thus have a substantial impact on your website’s performance.
Since 54 percent of customers prefer to see videos on your website, it’s crucial for your business that you can provide them in high resolution.
Control over asset delivery
When a CDN monitors your asset delivery, operators can determine where extra capacity is needed, based on real-time statistics. If the server in a certain region is suffering from overload, operators can provide extra bandwidth to make sure that everything is running smoothly.
Protection against traffic spikes
If your website suddenly experiences a large inflow of traffic, you can benefit from CDN services. A large network of servers ensures that these resources are available and scalable in all cases. It’s a nightmare of many businesses that they will get a major increase in traffic, but their website cannot handle it.
Disadvantages of Using a CDN
Costs
This is perhaps the most significant downside to using a CDN. It’s expensive to start using CDN services, and they can also have many hidden costs. These include costs per each data transfer and gigabyte.
The high costs result from third-party networks. Starting up a new CDN network requires that a server company receive help from another company to install such a network. Be sure to read all terms and conditions carefully.
Given that, CDN networks tend to be a better option for large companies who can afford such costs. Maintaining replicate servers around the globe that are not useful is also impractical.
Location of services
If most of your audience is located in a country where the CDN has no servers, the data on your website may have to travel further than without using any CDN.
Do your research to find out where all the servers of the CDN provider are located. You don’t want to pay for servers that are located in places that will only reduce the performance of your website and increase latency and downtime for your customers.
Restrictions
Some organizations and countries have blocked the domains or IP addresses of popular CDNs. In this case, your audience from these organizations or countries cannot access your website, and you will end up losing some of your traffic.
Keep in mind that your CDN files will not work either if you’re developing offline.
Support availability
The question of support arises when a third-party vendor is responsible for running the CDN. In case of a technical issue, even if rare, you cannot know how long it takes for the operator to fix the problem and prevent it from happening again.
Loss of control
Do you feel comfortable handing over your website files to another company? This is something that you must consider before deciding whether to use a CDN or not. Using a CDN means that third parties receive information about your website and systems.
Additional risks
CDNs can fail, too. If your CDN goes out of business, you have to move your website to another host. Also, if the service is unavailable, it’s impossible to use your CDN and fall back to local files. While not common, there are additional risks that you should take into account.
Conclusion
The question of whether you should use a CDN or not depends on the needs of your company. If you have a popular website with high traffic and enough resources, it will pay off. In return for the cost, you will get a faster website and an additional layer of security.
