
How To Discover Yourself Through Life Experiences
January 25, 2016
Then vs. Now: File Sharing
January 27, 2016We know, we know—an FTP blog?
There’s been some scuttlebut recently about transfer protocols that we thought we’d write up a little something to help internet users and website builders alike. In this blog, we’re going to discuss what FTP is, how it works, how it can help you, and the main difference between it and other transfer protocols like HTTP.
Let’s go!
What Does FTP Stand For?
FTP stands for File Transfter Protocol. And what it does is transfer files between computers. A fun fact about FTP is that it can be either a noun or a verb. As a noun, it stands for the program that sends files and as a method for sending the files. As a verb it would be as a means to send or receive (fetch) files.
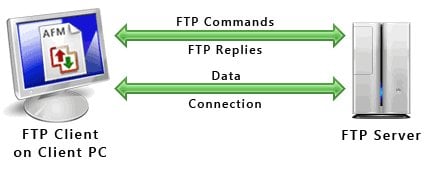
So, basically, it’s just a means for sending files, securely, from one machine (typically a server) to another. FTP is mainly used for the transfer of large files.
How Does FTP Work?
If you are looking to build a website, you will have to learn how to use FTP. FTP or file transfer protocol, is basically a client that allows you to transfer files from one location to another.
In a website context, you’ll be using FTP to transfer files on your computer to files on the server that your site is being hosted on. FTP clients have many options, but the following are five things you need to know to get started.
FTP Account
The first step of using your FTP client is setting up an account. In order to make an FTP client work with your hosting, you’ll have to login to your hosting account. Find the link in the hosting control panel where you can control the FTP options, and create a username and password. Make sure that you write down the hosting server address. We’ll talk about some FTP programs a little bit below, so please be aware that this is typically the path to follow, but some programs may be different. If you want to start now, give Filezilla a try!
Adding Sites to Your FTP Client
Once you’ve set up the information on your hosting control panel, you can start adding your site or sites to your FTP client. Go to the site manager and create a site profile. You’ll have to put in your username, password and hosting server address to complete the profile. Now your FTP client will be connected to your hosting account. Just make sure you click connect. Make sure your password is strong. If it’s easily guessable, all your information is up for grabs. This is how your website will be generated, if that’s what the purpose of your FTP is. All your CSS and other things can be hosted on your FTP client to be accessible from anywhere, i.e. so that you can host your website independently from where your local FTP files are.
Changing File or Directory Permissions and Attributes

Permissions and attributes are important for security measures as well as installing scripts. You can make changes by right clicking a file or folder and clicking properties. A window box will open up showing you the directory value, which is shown as 3 numeric numbers (usually 755). It will also show you read, write and executable options. The default settings are usually set up so that users cannot edit the file or folders.
Making Edits to Files
If you are working with an HTML or PHP file, you’ll frequently find yourself making edits to the code. Rather than editing on your desktop and rewriting the previous file, you can actually edit the file on the server. All you have to do is make sure that the admin has read and write privileges, and click edit to make the changes.
Creating New Folders and Batching File Downloads/Uploads
To create a new folder, all you have to do is to click the “add new folder” option in your client and name it. You can also download and upload multiple files at a time rather than doing one file at a time. Simply hold shift and click on the files you want to move. This will highlight the files. Then, transfer the files where you want them to go or drag and drop the highlighted files if the FTP client allows that option.
Let’s take a break and give a little metaphor here. FTP accesses your website differently than an internet user would. That makes sense because your website would have different entrances, just like a department store. While the customers come in from the front entrance, the FTP would knock on the shipping bay doors and be let in through the back (where customer aren’t allowed).
Batching allows you to do something else while you wait for files to be downloaded or uploaded. However, trying to move a whole folder can create problems with many FTP clients. When you want to transfer a whole folder, it’s a good idea to create a separate folder name and transfer all the individual files into that folder name. This will reduce download/upload time, reduce crashes, and make it easier to continue where you left off if something happens.
What Is an FTP Program?
An FTP program is the organizer of what data wants to be transmitted through FTP. The most popular FTP hosting software would be Filezilla which has useful features such as search and keeps everything well organized. The security of your ftp host software is important as well. Most popular software will be quite secure, Filezilla being no exception.
On an FTP program, users upload the data that they want to access from anywhere and secure it with a password. They can use that password to access and download the files from just about any machine.
What’s the Difference between FTP and HTTP?
While they are basically unrelated, FTP and HTTP do similar things.
HTTPis designed and intended for web browsers. It allows resources to get pulled from a website and displayed onto your screen, and it allows for data to be inputted onto the website itself.

Both you, the client, and the server, the website, transfer data back and forth (cookies). Now, when you’re interacting with a website and you want to download something, the website gathers that data from an FTP server and connects you, through HTTP, to that server to download it.
HTTP, is just another way data is transferred across machines, but FTP is still required to download large files. HTTP just can’t do it. That’s why websites keep themselves light to ensure faster browsing speeds.
Hopefully now you know a little bit more about FTP systems and how they interact with users around the internet. If you have any questions, please feel free to reach out to us and we’d love to help you! Comment below!
