
Why Data Centers Are Important for the Retail Industry
December 13, 2018
Smart Homes: Past, Present, and Future
December 18, 2018What Is TCP?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) widely known as Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of communications protocols used over the internet for delivery of services or packets within or across the network. It is commonly known as internet protocol suite.
The TCP/IP protocol consists of four layers such as link layer, network layer, transport layer, and application layer. Each layer adds addresses to the protocol stack as a physical address, logical address, port address, and application-specific address.
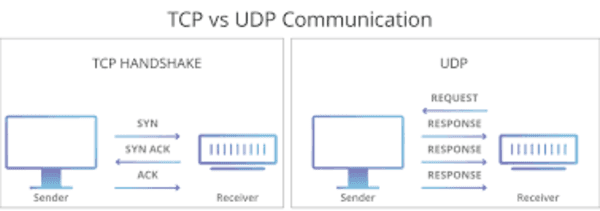
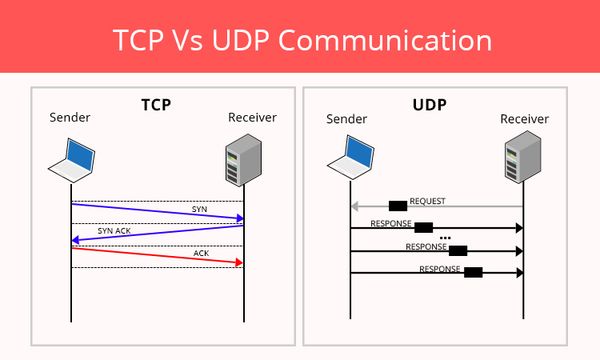
TCP is a connection-oriented point-to-point transport communication protocol that sends data packets as an unstructured stream of bytes in an ordered sequence. TCP provides information from sending node about the delivery of packets transmitted to a destination node by using sequence numbers and acknowledgment messages. TCP ensures reliability, end-to-end delivery, resequencing and retransmitting of data until a timeout condition is reached or acknowledgment of data packets is received.
Also, TCP offers flow control mechanism to sustain high transmission of packets over a speeding network as well as TCP protocols offer error detection and lost data features by trigging retransmission of data packets until an error-free acknowledgment is received. The TCP/IP protocol maintains communication with application layer protocols such as (FTP) file transfer protocol, (SMTP) simple mail transfer protocol, and (HTTP) hypertext transfer protocol.
What Is UDP?
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a connectionless transport layer communication protocol used to establish low tolerating and loss latency connections for delivery of services or packets within or across the network. It is coupled with an internet protocol suite as an alternative to TCP/IP protocol. Since UDP protocol is simple protocol, the retransmissions of packets can be decided at sender’s end whether to trade low latency for high reliability over data transmission. UDP reduces overall network traffic owing to network broadcasts feature which broadcasts packets to some computers on the same network and eliminates the need for duplication across the network. As UDP is connectionless protocol, the delivery or order of the data content packets varies.
UDP conjunctions with higher level protocols such as trivial file transfer protocol, real-time streaming protocol, simple network protocol, and domain name system lookups to manage data transmission services across the network.
TCP Vs. UDP
Data Transfer Features
TCP enables the establishment of a strong connection between two hosts to exchange data in streams. TCP guarantees to deliver data in the same ordered manner as sent from server to user and vice versa. Thus, TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. However, UDP is connectionless and non-dedicated protocol does not check the readiness of the receiver host.
Reliability
Reliability of TCP is comparatively higher as it ensures message acknowledgment and retransmissions of data in case of loss of data parts in transit. Hence, the hosts do not lose any missing data. On the other hand, UDP does not offer concepts of message acknowledgments, time-out or retransmission feature. Therefore, there is no communication of whether the packets have reached receiver or lost in transit.
Sequence
TCP transmits data packets in the same sequence as received. In case data packets are arriving in the wrong order, TCP reorders them and delivers in the correct order. In case of UDP, messages sent in a particular sequence may or may not be maintained while delivering the host. Therefore, the sequence or order in which packets will be transmitted is unpredictable.
Connection
A TCP connection is heavyweight, and it requires almost three packets for an appropriate socket connection and handles the congestion control and reliable delivery. UDP connection, on the other hand, is lightweight and transports layers designed over a particular IP. No connections are tracking or ordering of messages.
Data Streaming
Transmission Control Protocol reads data as streams of bytes, and the message is transmitted to segment boundaries. UDP messages contain packets that were sent one by one and are checked for integrity at the time of arrival.
Transfer Speed
The speed of TCP is slower as compared to UDP as it checks for errors and retransmits the packets.
Header Size
TCP’s size of the header is 20 bytes, whereas, UDP is 8 bytes. However, they have common header fields that are, source point, destination point, and checksum.
Usage by Other Protocols
Use by other protocols FTP, SMTP, HTTP, HTTPs, Telnet use TCP Protocols, and UDP protocols are used by TFTP, SNMP, DNS, DHCP, RIP, VOIP.
Detection of Errors
Transmission Control Protocol detects errors via checksum and performs error recovery. If any of the packets are erroneous, they do not get acknowledged by the receiver, which in turn triggers re-transmission by host/sender.
This mechanism is known as PAR (Positive Acknowledgement with Retransmission). Since TCP is slower than UDP, TCP is appropriate for applications that do not require high speed or longer period took for transmission is not a constraint.
Regarding error detection and error recovery, UDP works on a best effort basis. This protocol also supports error detection. However, the erroneous packets detected by checksum are discarded. UDP does not attempt to retransmit packets.
The reason UDP does not attempt retransmission of packets is that this protocol is commonly used for time-sensitive applications such as voice transmission, gaming, etc. Hence, recovery attempt would be of no point as by the time retransmission takes place, and the packets are received, they will be of no use.
Opportunities for TCP
As the TCP internet protocol suite is non-proprietary and offers reliable full-duplex connections with TCP Streams, 3-way handshake, credit flow control, fast retransmission and recovery, Selective-ACK, and scaling it is compatible with all operating systems available in the global market, as well as it is also compatible with all types of computer hardware and networks. This, in turn, generates huge opportunities for various players in the global market to adopt TCP internet protocol suite.
Opportunities for UDP
The UDP reduces the requirement of computer resources, thus, lowering the overhead, which results in high usage over small networks for multicast or broadcast of real-time packets transmissions. This is expected to create demand for small-scale networks over high transmission speed thereby generating opportunities in the global market.