What Fits Your Goal? Containers vs. Virtual Machines
August 27, 2019
How 2FA Can Protect My Data
August 29, 2019The IT world is comprised of many factors which all work together to make great things happen — say, us writing this article and you reading it. While some of these factors are evident and can be interacted with (designs and interfaces, for instance), the backbone (especially what happens inside internet connections) often seems like black magic for many people.
One of the most interesting internet-related technologies is the proxy server. Carrying various functionality, it helps dozens of millions of people make their internet connection more secure. Few people, however, stop to wonder how exactly it works; what are its benefits? What are its use cases? In this article, we will examine the intricacies of proxy servers and outline why you might want to start using one today. https://www.youtube.com/embed/Dk7h_stCXb0
Misconceptions
To better understand what a proxy server is, we should start with defining what a proxy server is not. First of all, it’s not “for the paranoid”: Internet security is a topic that should concern all online users, and proxy servers can provide precisely this type of security. Additionally, they allow for enhanced privacy, which is a fundamental human right. Nowadays, however, targeted advertisements, cookies, trackers, and malware are continually infringing users’ privacy and compromising their security — and proxy servers serve as fortresses guarding against this.
Secondly, it’s not for “malicious hackers”: proxy servers aren’t designed to hide dangerous activities carried out by hackers or terrorists; instead, they’re aimed at helping ordinary users make their browsing experience smoother and safer.
Thirdly, it’s not for “tech geeks”: although this topic might seem complicated, the fundamental principles of how proxy servers work (and their overall importance) are pretty easy to grasp — we’ll highlight this in the later sections of this article.
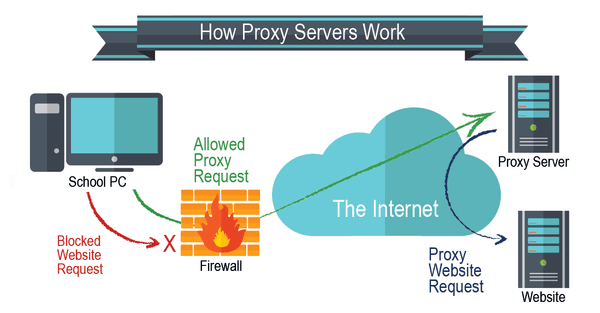
What Does a Proxy Server Do?
At its core, it functions as a third party between the client (e.g., an online user) and the service (e.g., this very website). A proxy server manages the requests sent by the client and completes them depending on the user’s preferences. This process usually happens in three steps:

- The user sends the request to the proxy server (as if saying “I need to access the information from, say, this weather app”).
- The proxy server retrieves the information…
- … and sends it to the user.
This technical definition may seem confusing, so we can re-explain it with a neat metaphor. Let’s imagine that you have a really smart dog trained to carry various objects from one person to the other. A friend comes for a visit to your house, so you give your dog a box of chocolates and ask her to give this box to them.
The dog completes the delivery, and your friend understands that the box is actually a gift from you (but not from someone who simply carried this box) — it still has your fingerprints and perfume, complete with packaging and a personal letter written by you. The only difference is the messenger, and soon we’ll learn why.
A proxy server, however, is unable to encrypt the client’s data which makes the user vulnerable to interventions from hackers, local governments, and internet service providers.
Proxies are interlinked with another internet technology — Virtual Private Networks, so it makes perfect sense to illustrate how VPNs work while we’re at it. If the messenger dog from the metaphor we’ve used above acted as a VPN, our friend would receive the contents, i.e., chocolates themselves, without any packaging which can help to identify the sender. This is where the most crucial distinction lies: VPNs are designed to make the contents anonymous.
What Are the Benefits Associated with Using a Proxy Server?
The process of setting up, configuring, and maintaining an internet connection via a proxy server might seem cumbersome — but the benefits are worth it. First of all, privacy: you can hide your IP address, which otherwise would be visible and could be hijacked when visiting a website. Even though the user’s public IP address may seem like a useless collection of arbitrary numbers, exposing it introduces a whole plethora of security concerns.

Another benefit has to do with speed and performance: proxy servers can compress the user’s traffic, allowing for increased internet bandwidth. Additionally, they can cache individual web pages, store them in their databases, and serve them to their users — obviously, loading cached versions are much quicker on the user’s end.
Use Cases
Boasting numerous benefits, proxy servers can easily highlight why you should start using one with some real-world use cases. One example would be gaining access to blocked websites: it’s not uncommon for ISPs (and various governments) to restrict access to multiple sites. Sometimes they’re blocked for a reason: torrent websites, for instance, cause countless cases of copyright infringement.
Other websites and services, however, may choose not to comply with the given country’s national law and become blocked on these grounds. A striking example would be the 2016 case against LinkedIn, which was blocked in Russia due to not complying with the newly introduced data retention law. Ordinary users suffered because, overnight, they no longer had access to the world’s largest professional network. In this scenario, they were forced to utilize proxy servers to restore access and continue (net)working.
Another compelling use case is logging activity and restricting access, which, combined with… wait — didn’t we just say that restricting access is a double-edged sword? Indeed — but this feature can be used by companies to block access to the web-resources that may contain malicious content. While ordinary employees may not be aware that Website X is unsafe, company webmasters and system administrators can block it to save the company thousands of dollars possibly.
Conclusion
Like all other internet technologies, proxy servers often seem incredibly complicated and hard to understand. We cannot say they’re as easy as basic maths — but with just enough perseverance, you can master them and utilize the benefits they offer to make your online environment a safer place.
Main Photo Credit: whatismyipaddress.com
1 Comment
[…] for hosting both mobile and traditional data center proxies. These centers enhance security with robust physical and cybersecurity measures, including advanced surveillance and controlled access. These features are essential for protecting […]